深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索广泛运用于树和图中,但是它们的应用远远不止如此。
BFS
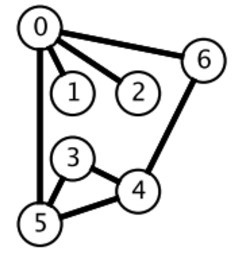
广度优先搜索一层一层地进行遍历,每层遍历都是以上一层遍历的结果作为起点,遍历一个距离能访问到的所有节点。需要注意的是,遍历过的节点不能再次被遍历。
第一层:
- 0 -> {6,2,1,5}
第二层:
- 6 -> {4}
- 2 -> {}
- 1 -> {}
- 5 -> {3}
第三层:
- 4 -> {}
- 3 -> {}
每一层遍历的节点都与根节点距离相同。设 di 表示第 i 个节点与根节点的距离,推导出一个结论:对于先遍历的节点 i 与后遍历的节点 j,有 di <= dj。利用这个结论,可以求解最短路径等 最优解 问题:第一次遍历到目的节点,其所经过的路径为最短路径。应该注意的是,使用 BFS 只能求解无权图的最短路径,无权图是指从一个节点到另一个节点的代价都记为 1。
在程序实现 BFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 队列:用来存储每一轮遍历得到的节点;
- 标记:对于遍历过的节点,应该将它标记,防止重复遍历。
1. 计算在网格中从原点到特定点的最短路径长度
1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix(Medium)
[[1,1,0,1],
[1,0,1,0],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,0,1,1]]
题目描述:0 表示可以经过某个位置,求解从左上角到右下角的最短路径长度。
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grids) {
if (grids == null || grids.length == 0 || grids[0].length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int[][] direction = {{1, -1}, {1, 0}, {1, 1}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}};
int m = grids.length, n = grids[0].length;
Queue<Pair<Integer, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair<>(0, 0));
int pathLength = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
pathLength++;
while (size-- > 0) {
Pair<Integer, Integer> cur = queue.poll();
int cr = cur.getKey(), cc = cur.getValue();
if (grids[cr][cc] == 1) {
continue;
}
if (cr == m - 1 && cc == n - 1) {
return pathLength;
}
grids[cr][cc] = 1; // 标记
for (int[] d : direction) {
int nr = cr + d[0], nc = cc + d[1];
if (nr < 0 || nr >= m || nc < 0 || nc >= n) {
continue;
}
queue.add(new Pair<>(nr, nc));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
2. 组成整数的最小平方数数量
279. Perfect Squares (Medium)
For example, given n = 12, return 3 because 12 = 4 + 4 + 4; given n = 13, return 2 because 13 = 4 + 9.
可以将每个整数看成图中的一个节点,如果两个整数之差为一个平方数,那么这两个整数所在的节点就有一条边。
要求解最小的平方数数量,就是求解从节点 n 到节点 0 的最短路径。
本题也可以用动态规划求解,在之后动态规划部分中会再次出现。
public int numSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> squares = generateSquares(n);
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] marked = new boolean[n + 1];
queue.add(n);
marked[n] = true;
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
level++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (int s : squares) {
int next = cur - s;
if (next < 0) {
break;
}
if (next == 0) {
return level;
}
if (marked[next]) {
continue;
}
marked[next] = true;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return n;
}
/**
* 生成小于 n 的平方数序列
* @return 1,4,9,...
*/
private List<Integer> generateSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> squares = new ArrayList<>();
int square = 1;
int diff = 3;
while (square <= n) {
squares.add(square);
square += diff;
diff += 2;
}
return squares;
}
3. 最短单词路径
127. Word Ladder (Medium)
Input:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Output: 5
Explanation: As one shortest transformation is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
return its length 5.
Input:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Output: 0
Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore no possible transformation.
题目描述:找出一条从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短路径,每次移动规定为改变一个字符,并且改变之后的字符串必须在 wordList 中。
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
wordList.add(beginWord);
int N = wordList.size();
int start = N - 1;
int end = 0;
while (end < N && !wordList.get(end).equals(endWord)) {
end++;
}
if (end == N) {
return 0;
}
List<Integer>[] graphic = buildGraphic(wordList);
return getShortestPath(graphic, start, end);
}
private List<Integer>[] buildGraphic(List<String> wordList) {
int N = wordList.size();
List<Integer>[] graphic = new List[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
graphic[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (isConnect(wordList.get(i), wordList.get(j))) {
graphic[i].add(j);
}
}
}
return graphic;
}
private boolean isConnect(String s1, String s2) {
int diffCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length() && diffCnt <= 1; i++) {
if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) {
diffCnt++;
}
}
return diffCnt == 1;
}
private int getShortestPath(List<Integer>[] graphic, int start, int end) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] marked = new boolean[graphic.length];
queue.add(start);
marked[start] = true;
int path = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
path++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (int next : graphic[cur]) {
if (next == end) {
return path;
}
if (marked[next]) {
continue;
}
marked[next] = true;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
DFS
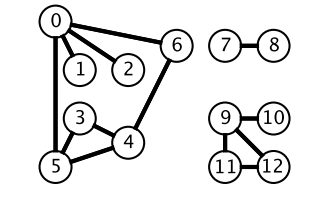
广度优先搜索一层一层遍历,每一层得到的所有新节点,要用队列存储起来以备下一层遍历的时候再遍历。
而深度优先搜索在得到一个新节点时立即对新节点进行遍历:从节点 0 出发开始遍历,得到到新节点 6 时,立马对新节点 6 进行遍历,得到新节点 4;如此反复以这种方式遍历新节点,直到没有新节点了,此时返回。返回到根节点 0 的情况是,继续对根节点 0 进行遍历,得到新节点 2,然后继续以上步骤。
从一个节点出发,使用 DFS 对一个图进行遍历时,能够遍历到的节点都是从初始节点可达的,DFS 常用来求解这种 可达性 问题。
在程序实现 DFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 栈:用栈来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归栈。
- 标记:和 BFS 一样同样需要对已经遍历过的节点进行标记。
1. 查找最大的连通面积
695. Max Area of Island (Medium)
[[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
private int m, n;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, dfs(grid, i, j));
}
}
return maxArea;
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || grid[r][c] == 0) {
return 0;
}
grid[r][c] = 0;
int area = 1;
for (int[] d : direction) {
area += dfs(grid, r + d[0], c + d[1]);
}
return area;
}
2. 矩阵中的连通分量数目
200. Number of Islands (Medium)
Input:
11000
11000
00100
00011
Output: 3
可以将矩阵表示看成一张有向图。
private int m, n;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
int islandsNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] != '0') {
dfs(grid, i, j);
islandsNum++;
}
}
}
return islandsNum;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || grid[i][j] == '0') {
return;
}
grid[i][j] = '0';
for (int[] d : direction) {
dfs(grid, i + d[0], j + d[1]);
}
}
3. 好友关系的连通分量数目
547. Friend Circles (Medium)
Input:
[[1,1,0],
[1,1,0],
[0,0,1]]
Output: 2
Explanation:The 0th and 1st students are direct friends, so they are in a friend circle.
The 2nd student himself is in a friend circle. So return 2.
题目描述:好友关系可以看成是一个无向图,例如第 0 个人与第 1 个人是好友,那么 M[0][1] 和 M[1][0] 的值都为 1。
private int n;
public int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
n = M.length;
int circleNum = 0;
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!hasVisited[i]) {
dfs(M, i, hasVisited);
circleNum++;
}
}
return circleNum;
}
private void dfs(int[][] M, int i, boolean[] hasVisited) {
hasVisited[i] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
if (M[i][k] == 1 && !hasVisited[k]) {
dfs(M, k, hasVisited);
}
}
}
4. 填充封闭区域
130. Surrounded Regions (Medium)
For example,
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
After running your function, the board should be:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
题目描述:使被 'X' 包围的 'O' 转换为 'X'。
先填充最外侧,剩下的就是里侧了。
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
private int m, n;
public void solve(char[][] board) {
if (board == null || board.length == 0) {
return;
}
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(board, i, 0);
dfs(board, i, n - 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(board, 0, i);
dfs(board, m - 1, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'T') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
} else if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
private void dfs(char[][] board, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || board[r][c] != 'O') {
return;
}
board[r][c] = 'T';
for (int[] d : direction) {
dfs(board, r + d[0], c + d[1]);
}
}
5. 能到达的太平洋和大西洋的区域
417. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow (Medium)
Given the following 5x5 matrix:
Pacific ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *
~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *
~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 *
~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *
~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *
* * * * * Atlantic
Return:
[[0, 4], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 2], [3, 0], [3, 1], [4, 0]] (positions with parentheses in above matrix).
左边和上边是太平洋,右边和下边是大西洋,内部的数字代表海拔,海拔高的地方的水能够流到低的地方,求解水能够流到太平洋和大西洋的所有位置。
private int m, n;
private int[][] matrix;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {
return ret;
}
m = matrix.length;
n = matrix[0].length;
this.matrix = matrix;
boolean[][] canReachP = new boolean[m][n];
boolean[][] canReachA = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(i, 0, canReachP);
dfs(i, n - 1, canReachA);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(0, i, canReachP);
dfs(m - 1, i, canReachA);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (canReachP[i][j] && canReachA[i][j]) {
ret.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));
}
}
}
return ret;
}
private void dfs(int r, int c, boolean[][] canReach) {
if (canReach[r][c]) {
return;
}
canReach[r][c] = true;
for (int[] d : direction) {
int nextR = d[0] + r;
int nextC = d[1] + c;
if (nextR < 0 || nextR >= m || nextC < 0 || nextC >= n
|| matrix[r][c] > matrix[nextR][nextC]) {
continue;
}
dfs(nextR, nextC, canReach);
}
}
Backtracking
Backtracking(回溯)属于 DFS。
- 普通 DFS 主要用在 可达性问题 ,这种问题只需要执行到特点的位置然后返回即可。
- 而 Backtracking 主要用于求解 排列组合 问题,例如有 { 'a','b','c' } 三个字符,求解所有由这三个字符排列得到的字符串,这种问题在执行到特定的位置返回之后还会继续执行求解过程。
因为 Backtracking 不是立即返回,而要继续求解,因此在程序实现时,需要注意对元素的标记问题:
- 在访问一个新元素进入新的递归调用时,需要将新元素标记为已经访问,这样才能在继续递归调用时不用重复访问该元素;
- 但是在递归返回时,需要将元素标记为未访问,因为只需要保证在一个递归链中不同时访问一个元素,可以访问已经访问过但是不在当前递归链中的元素。
1. 数字键盘组合
17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number (Medium)

Input:Digit string "23"
Output: ["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
private static final String[] KEYS = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
List<String> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0) {
return combinations;
}
doCombination(new StringBuilder(), combinations, digits);
return combinations;
}
private void doCombination(StringBuilder prefix, List<String> combinations, final String digits) {
if (prefix.length() == digits.length()) {
combinations.add(prefix.toString());
return;
}
int curDigits = digits.charAt(prefix.length()) - '0';
String letters = KEYS[curDigits];
for (char c : letters.toCharArray()) {
prefix.append(c); // 添加
doCombination(prefix, combinations, digits);
prefix.deleteCharAt(prefix.length() - 1); // 删除
}
}
2. IP 地址划分
93. Restore IP Addresses(Medium)
Given "25525511135",
return ["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"].
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
List<String> addresses = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder tempAddress = new StringBuilder();
doRestore(0, tempAddress, addresses, s);
return addresses;
}
private void doRestore(int k, StringBuilder tempAddress, List<String> addresses, String s) {
if (k == 4 || s.length() == 0) {
if (k == 4 && s.length() == 0) {
addresses.add(tempAddress.toString());
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length() && i <= 2; i++) {
if (i != 0 && s.charAt(0) == '0') {
break;
}
String part = s.substring(0, i + 1);
if (Integer.valueOf(part) <= 255) {
if (tempAddress.length() != 0) {
part = "." + part;
}
tempAddress.append(part);
doRestore(k + 1, tempAddress, addresses, s.substring(i + 1));
tempAddress.delete(tempAddress.length() - part.length(), tempAddress.length());
}
}
}
3. 在矩阵中寻找字符串
79. Word Search (Medium)
For example,
Given board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
word = "ABCCED", -> returns true,
word = "SEE", -> returns true,
word = "ABCB", -> returns false.
private final static int[][] direction = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
private int m;
private int n;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
if (word == null || word.length() == 0) {
return true;
}
if (board == null || board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
boolean[][] hasVisited = new boolean[m][n];
for (int r = 0; r < m; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (backtracking(0, r, c, hasVisited, board, word)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean backtracking(int curLen, int r, int c, boolean[][] visited, final char[][] board, final String word) {
if (curLen == word.length()) {
return true;
}
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n
|| board[r][c] != word.charAt(curLen) || visited[r][c]) {
return false;
}
visited[r][c] = true;
for (int[] d : direction) {
if (backtracking(curLen + 1, r + d[0], c + d[1], visited, board, word)) {
return true;
}
}
visited[r][c] = false;
return false;
}
4. 输出二叉树中所有从根到叶子的路径
257. Binary Tree Paths (Easy)
1
/ \
2 3
\
5
["1->2->5", "1->3"]
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return paths;
}
List<Integer> values = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(root, values, paths);
return paths;
}
private void backtracking(TreeNode node, List<Integer> values, List<String> paths) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
values.add(node.val);
if (isLeaf(node)) {
paths.add(buildPath(values));
} else {
backtracking(node.left, values, paths);
backtracking(node.right, values, paths);
}
values.remove(values.size() - 1);
}
private boolean isLeaf(TreeNode node) {
return node.left == null && node.right == null;
}
private String buildPath(List<Integer> values) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < values.size(); i++) {
str.append(values.get(i));
if (i != values.size() - 1) {
str.append("->");
}
}
return str.toString();
}
5. 排列
46. Permutations (Medium)
[1,2,3] have the following permutations:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> permutes = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> permuteList = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[nums.length];
backtracking(permuteList, permutes, hasVisited, nums);
return permutes;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> permuteList, List<List<Integer>> permutes, boolean[] visited, final int[] nums) {
if (permuteList.size() == nums.length) {
permutes.add(new ArrayList<>(permuteList)); // 重新构造一个 List
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
permuteList.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(permuteList, permutes, visited, nums);
permuteList.remove(permuteList.size() - 1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
6. 含有相同元素求排列
47. Permutations II (Medium)
[1,1,2] have the following unique permutations:
[[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]]
数组元素可能含有相同的元素,进行排列时就有可能出现重复的排列,要求重复的排列只返回一个。
在实现上,和 Permutations 不同的是要先排序,然后在添加一个元素时,判断这个元素是否等于前一个元素,如果等于,并且前一个元素还未访问,那么就跳过这个元素。
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> permutes = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> permuteList = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums); // 排序
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[nums.length];
backtracking(permuteList, permutes, hasVisited, nums);
return permutes;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> permuteList, List<List<Integer>> permutes, boolean[] visited, final int[] nums) {
if (permuteList.size() == nums.length) {
permutes.add(new ArrayList<>(permuteList));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++) {
if (i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !visited[i - 1]) {
continue; // 防止重复
}
if (visited[i]){
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
permuteList.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(permuteList, permutes, visited, nums);
permuteList.remove(permuteList.size() - 1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
7. 组合
77. Combinations (Medium)
If n = 4 and k = 2, a solution is:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> combineList = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(combineList, combinations, 1, k, n);
return combinations;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> combineList, List<List<Integer>> combinations, int start, int k, final int n) {
if (k == 0) {
combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(combineList));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= n - k + 1; i++) { // 剪枝
combineList.add(i);
backtracking(combineList, combinations, i + 1, k - 1, n);
combineList.remove(combineList.size() - 1);
}
}
8. 组合求和
39. Combination Sum (Medium)
given candidate set [2, 3, 6, 7] and target 7,
A solution set is:
[[7],[2, 2, 3]]
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(new ArrayList<>(), combinations, 0, target, candidates);
return combinations;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> tempCombination, List<List<Integer>> combinations,
int start, int target, final int[] candidates) {
if (target == 0) {
combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(tempCombination));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (candidates[i] <= target) {
tempCombination.add(candidates[i]);
backtracking(tempCombination, combinations, i, target - candidates[i], candidates);
tempCombination.remove(tempCombination.size() - 1);
}
}
}
9. 含有相同元素的组合求和
40. Combination Sum II (Medium)
For example, given candidate set [10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5] and target 8,
A solution set is:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtracking(new ArrayList<>(), combinations, new boolean[candidates.length], 0, target, candidates);
return combinations;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> tempCombination, List<List<Integer>> combinations,
boolean[] hasVisited, int start, int target, final int[] candidates) {
if (target == 0) {
combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(tempCombination));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (i != 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !hasVisited[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
if (candidates[i] <= target) {
tempCombination.add(candidates[i]);
hasVisited[i] = true;
backtracking(tempCombination, combinations, hasVisited, i + 1, target - candidates[i], candidates);
hasVisited[i] = false;
tempCombination.remove(tempCombination.size() - 1);
}
}
}
10. 1-9 数字的组合求和
216. Combination Sum III (Medium)
Input: k = 3, n = 9
Output:
[[1,2,6], [1,3,5], [2,3,4]]
从 1-9 数字中选出 k 个数不重复的数,使得它们的和为 n。
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(k, n, 1, path, combinations);
return combinations;
}
private void backtracking(int k, int n, int start,
List<Integer> tempCombination, List<List<Integer>> combinations) {
if (k == 0 && n == 0) {
combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(tempCombination));
return;
}
if (k == 0 || n == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= 9; i++) {
tempCombination.add(i);
backtracking(k - 1, n - i, i + 1, tempCombination, combinations);
tempCombination.remove(tempCombination.size() - 1);
}
}
11. 子集
78. Subsets (Medium)
找出集合的所有子集,子集不能重复,[1, 2] 和 [2, 1] 这种子集算重复
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> subsets = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tempSubset = new ArrayList<>();
for (int size = 0; size <= nums.length; size++) {
backtracking(0, tempSubset, subsets, size, nums); // 不同的子集大小
}
return subsets;
}
private void backtracking(int start, List<Integer> tempSubset, List<List<Integer>> subsets,
final int size, final int[] nums) {
if (tempSubset.size() == size) {
subsets.add(new ArrayList<>(tempSubset));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
tempSubset.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(i + 1, tempSubset, subsets, size, nums);
tempSubset.remove(tempSubset.size() - 1);
}
}
12. 含有相同元素求子集
90. Subsets II (Medium)
For example,
If nums = [1,2,2], a solution is:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> subsets = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tempSubset = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[nums.length];
for (int size = 0; size <= nums.length; size++) {
backtracking(0, tempSubset, subsets, hasVisited, size, nums); // 不同的子集大小
}
return subsets;
}
private void backtracking(int start, List<Integer> tempSubset, List<List<Integer>> subsets, boolean[] hasVisited,
final int size, final int[] nums) {
if (tempSubset.size() == size) {
subsets.add(new ArrayList<>(tempSubset));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !hasVisited[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
tempSubset.add(nums[i]);
hasVisited[i] = true;
backtracking(i + 1, tempSubset, subsets, hasVisited, size, nums);
hasVisited[i] = false;
tempSubset.remove(tempSubset.size() - 1);
}
}
13. 分割字符串使得每个部分都是回文数
131. Palindrome Partitioning (Medium)
For example, given s = "aab",
Return
[
["aa","b"],
["a","a","b"]
]
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
List<List<String>> partitions = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> tempPartition = new ArrayList<>();
doPartition(s, partitions, tempPartition);
return partitions;
}
private void doPartition(String s, List<List<String>> partitions, List<String> tempPartition) {
if (s.length() == 0) {
partitions.add(new ArrayList<>(tempPartition));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, 0, i)) {
tempPartition.add(s.substring(0, i + 1));
doPartition(s.substring(i + 1), partitions, tempPartition);
tempPartition.remove(tempPartition.size() - 1);
}
}
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int begin, int end) {
while (begin < end) {
if (s.charAt(begin++) != s.charAt(end--)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
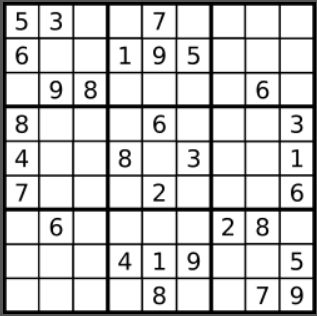
14. 数独
37. Sudoku Solver (Hard)
private boolean[][] rowsUsed = new boolean[9][10];
private boolean[][] colsUsed = new boolean[9][10];
private boolean[][] cubesUsed = new boolean[9][10];
private char[][] board;
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
this.board = board;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
continue;
}
int num = board[i][j] - '0';
rowsUsed[i][num] = true;
colsUsed[j][num] = true;
cubesUsed[cubeNum(i, j)][num] = true;
}
backtracking(0, 0);
}
private boolean backtracking(int row, int col) {
while (row < 9 && board[row][col] != '.') {
row = col == 8 ? row + 1 : row;
col = col == 8 ? 0 : col + 1;
}
if (row == 9) {
return true;
}
for (int num = 1; num <= 9; num++) {
if (rowsUsed[row][num] || colsUsed[col][num] || cubesUsed[cubeNum(row, col)][num]) {
continue;
}
rowsUsed[row][num] = colsUsed[col][num] = cubesUsed[cubeNum(row, col)][num] = true;
board[row][col] = (char) (num + '0');
if (backtracking(row, col)) {
return true;
}
board[row][col] = '.';
rowsUsed[row][num] = colsUsed[col][num] = cubesUsed[cubeNum(row, col)][num] = false;
}
return false;
}
private int cubeNum(int i, int j) {
int r = i / 3;
int c = j / 3;
return r * 3 + c;
}
15. N 皇后
51. N-Queens (Hard)
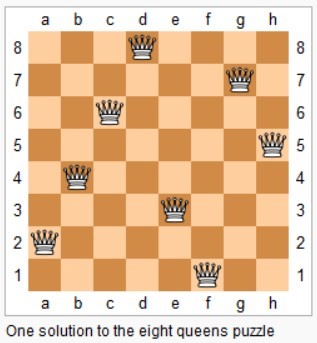
在 n*n 的矩阵中摆放 n 个皇后,并且每个皇后不能在同一行,同一列,同一对角线上,求所有的 n 皇后的解。
一行一行地摆放,在确定一行中的那个皇后应该摆在哪一列时,需要用三个标记数组来确定某一列是否合法,这三个标记数组分别为:列标记数组、45 度对角线标记数组和 135 度对角线标记数组。
45 度对角线标记数组的长度为 2 * n - 1,通过下图可以明确 (r, c) 的位置所在的数组下标为 r + c。
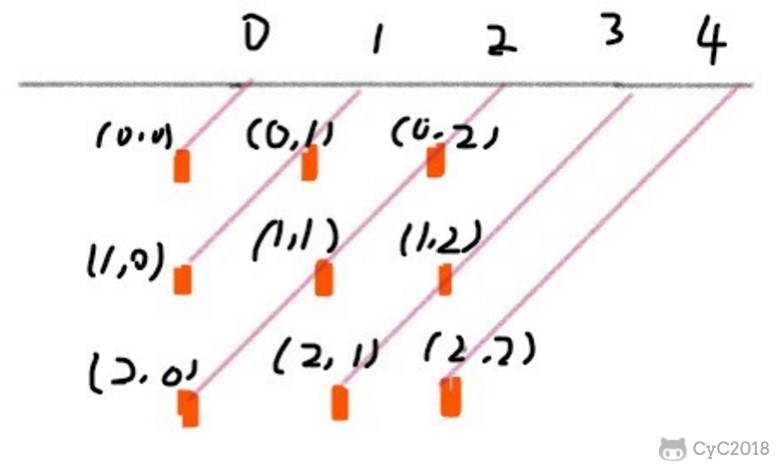
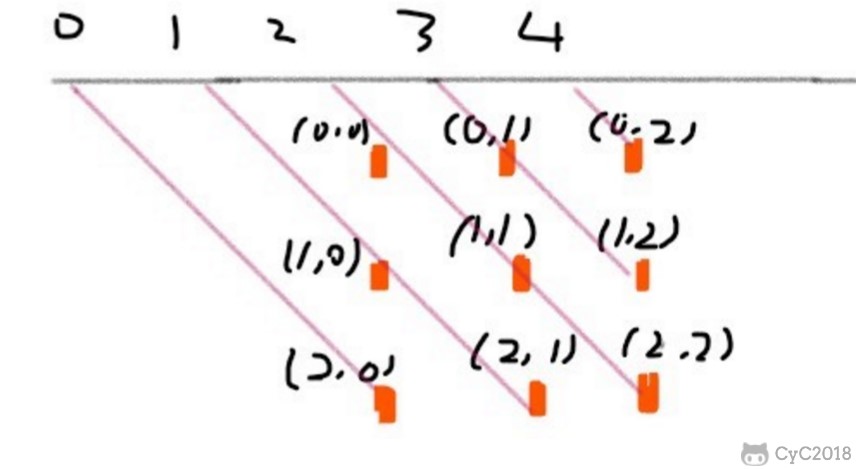
135 度对角线标记数组的长度也是 2 * n - 1,(r, c) 的位置所在的数组下标为 n - 1 - (r - c)。
private List<List<String>> solutions;
private char[][] nQueens;
private boolean[] colUsed;
private boolean[] diagonals45Used;
private boolean[] diagonals135Used;
private int n;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
solutions = new ArrayList<>();
nQueens = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(nQueens[i], '.');
}
colUsed = new boolean[n];
diagonals45Used = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
diagonals135Used = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
this.n = n;
backtracking(0);
return solutions;
}
private void backtracking(int row) {
if (row == n) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] chars : nQueens) {
list.add(new String(chars));
}
solutions.add(list);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
int diagonals45Idx = row + col;
int diagonals135Idx = n - 1 - (row - col);
if (colUsed[col] || diagonals45Used[diagonals45Idx] || diagonals135Used[diagonals135Idx]) {
continue;
}
nQueens[row][col] = 'Q';
colUsed[col] = diagonals45Used[diagonals45Idx] = diagonals135Used[diagonals135Idx] = true;
backtracking(row + 1);
colUsed[col] = diagonals45Used[diagonals45Idx] = diagonals135Used[diagonals135Idx] = false;
nQueens[row][col] = '.';
}
}