- 1. 分配饼干
- 2. 不重叠的区间个数
- 3. 投飞镖刺破气球
- 4. 根据身高和序号重组队列
- 5. 买卖股票最大的收益
- 6. 买卖股票的最大收益 II
- 7. 种植花朵
- 8. 判断是否为子序列
- 9. 修改一个数成为非递减数组
- 10. 子数组最大的和
- 11. 分隔字符串使同种字符出现在一起
保证每次操作都是局部最优的,并且最后得到的结果是全局最优的。
1. 分配饼干
455. Assign Cookies (Easy)
Input: grid[1,3], size[1,2,4]
Output: 2
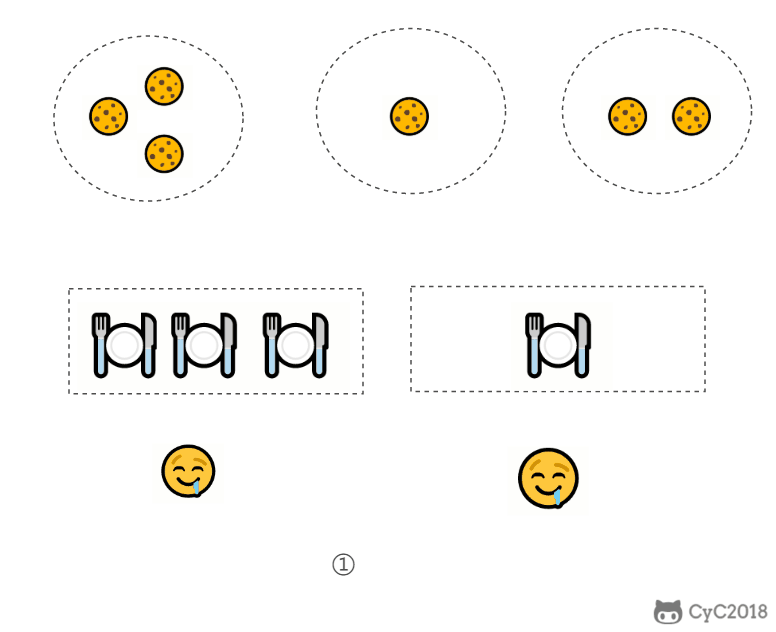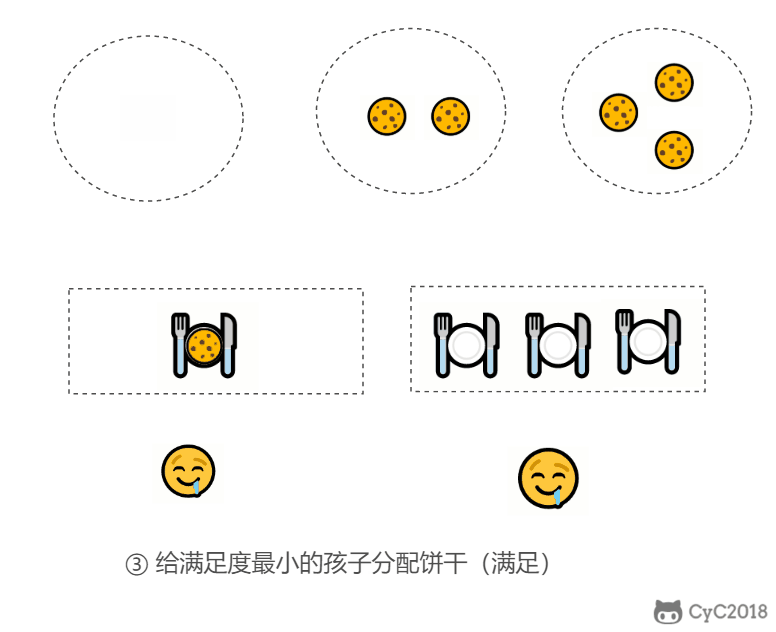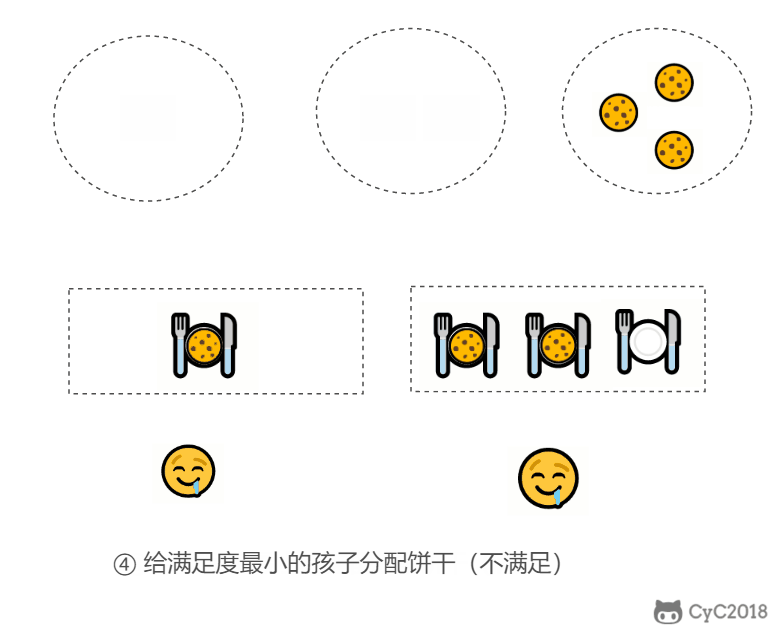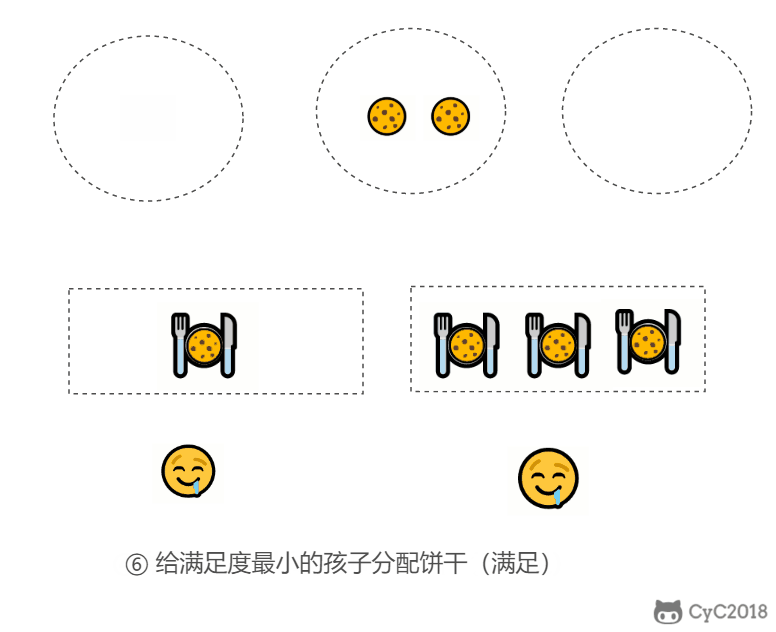
题目描述:每个孩子都有一个满足度 grid,每个饼干都有一个大小 size,只有饼干的大小大于等于一个孩子的满足度,该孩子才会获得满足。求解最多可以获得满足的孩子数量。
- 给一个孩子的饼干应当尽量小并且又能满足该孩子,这样大饼干才能拿来给满足度比较大的孩子。
- 因为满足度最小的孩子最容易得到满足,所以先满足满足度最小的孩子。
在以上的解法中,我们只在每次分配时饼干时选择一种看起来是当前最优的分配方法,但无法保证这种局部最优的分配方法最后能得到全局最优解。我们假设能得到全局最优解,并使用反证法进行证明,即假设存在一种比我们使用的贪心策略更优的最优策略。如果不存在这种最优策略,表示贪心策略就是最优策略,得到的解也就是全局最优解。
证明:假设在某次选择中,贪心策略选择给当前满足度最小的孩子分配第 m 个饼干,第 m 个饼干为可以满足该孩子的最小饼干。假设存在一种最优策略,可以给该孩子分配第 n 个饼干,并且 m < n。我们可以发现,经过这一轮分配,贪心策略分配后剩下的饼干一定有一个比最优策略来得大。因此在后续的分配中,贪心策略一定能满足更多的孩子。也就是说不存在比贪心策略更优的策略,即贪心策略就是最优策略。
public int findContentChildren(int[] grid, int[] size) {
if (grid == null || size == null) return 0;
Arrays.sort(grid);
Arrays.sort(size);
int gi = 0, si = 0;
while (gi < grid.length && si < size.length) {
if (grid[gi] <= size[si]) {
gi++;
}
si++;
}
return gi;
}
2. 不重叠的区间个数
435. Non-overlapping Intervals (Medium)
Input: [ [1,2], [1,2], [1,2] ]
Output: 2
Explanation: You need to remove two [1,2] to make the rest of intervals non-overlapping.
Input: [ [1,2], [2,3] ]
Output: 0
Explanation: You don't need to remove any of the intervals since they're already non-overlapping.
题目描述:计算让一组区间不重叠所需要移除的区间个数。
先计算最多能组成的不重叠区间个数,然后用区间总个数减去不重叠区间的个数。
在每次选择中,区间的结尾最为重要,选择的区间结尾越小,留给后面的区间的空间越大,那么后面能够选择的区间个数也就越大。
按区间的结尾进行排序,每次选择结尾最小,并且和前一个区间不重叠的区间。
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
if (intervals.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(intervals, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[1]));
int cnt = 1;
int end = intervals[0][1];
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
if (intervals[i][0] < end) {
continue;
}
end = intervals[i][1];
cnt++;
}
return intervals.length - cnt;
}
使用 lambda 表示式创建 Comparator 会导致算法运行时间过长,如果注重运行时间,可以修改为普通创建 Comparator 语句:
Arrays.sort(intervals, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[1] - o2[1];
}
});
3. 投飞镖刺破气球
452. Minimum Number of Arrows to Burst Balloons (Medium)
Input:
[[10,16], [2,8], [1,6], [7,12]]
Output:
2
题目描述:气球在一个水平数轴上摆放,可以重叠,飞镖垂直投向坐标轴,使得路径上的气球都被刺破。求解最小的投飞镖次数使所有气球都被刺破。
也是计算不重叠的区间个数,不过和 Non-overlapping Intervals 的区别在于,[1, 2] 和 [2, 3] 在本题中算是重叠区间。
public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
if (points.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(points, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[1]));
int cnt = 1, end = points[0][1];
for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
if (points[i][0] <= end) {
continue;
}
cnt++;
end = points[i][1];
}
return cnt;
}
4. 根据身高和序号重组队列
406. Queue Reconstruction by Height(Medium)
Input:
[[7,0], [4,4], [7,1], [5,0], [6,1], [5,2]]
Output:
[[5,0], [7,0], [5,2], [6,1], [4,4], [7,1]]
题目描述:一个学生用两个分量 (h, k) 描述,h 表示身高,k 表示排在前面的有 k 个学生的身高比他高或者和他一样高。
为了使插入操作不影响后续的操作,身高较高的学生应该先做插入操作,否则身高较小的学生原先正确插入的第 k 个位置可能会变成第 k+1 个位置。
身高 h 降序、个数 k 值升序,然后将某个学生插入队列的第 k 个位置中。
public int[][] reconstructQueue(int[][] people) {
if (people == null || people.length == 0 || people[0].length == 0) {
return new int[0][0];
}
Arrays.sort(people, (a, b) -> (a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : b[0] - a[0]));
List<int[]> queue = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] p : people) {
queue.add(p[1], p);
}
return queue.toArray(new int[queue.size()][]);
}
5. 买卖股票最大的收益
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock (Easy)
题目描述:一次股票交易包含买入和卖出,只进行一次交易,求最大收益。
只要记录前面的最小价格,将这个最小价格作为买入价格,然后将当前的价格作为售出价格,查看当前收益是不是最大收益。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if (n == 0) return 0;
int soFarMin = prices[0];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (soFarMin > prices[i]) soFarMin = prices[i];
else max = Math.max(max, prices[i] - soFarMin);
}
return max;
}
6. 买卖股票的最大收益 II
122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II (Easy)
题目描述:可以进行多次交易,多次交易之间不能交叉进行,可以进行多次交易。
对于 [a, b, c, d],如果有 a <= b <= c <= d ,那么最大收益为 d - a。而 d - a = (d - c) + (c - b) + (b - a) ,因此当访问到一个 prices[i] 且 prices[i] - prices[i-1] > 0,那么就把 prices[i] - prices[i-1] 添加到收益中。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
profit += (prices[i] - prices[i - 1]);
}
}
return profit;
}
7. 种植花朵
605. Can Place Flowers (Easy)
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 1
Output: True
题目描述:flowerbed 数组中 1 表示已经种下了花朵。花朵之间至少需要一个单位的间隔,求解是否能种下 n 朵花。
public boolean canPlaceFlowers(int[] flowerbed, int n) {
int len = flowerbed.length;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len && cnt < n; i++) {
if (flowerbed[i] == 1) {
continue;
}
int pre = i == 0 ? 0 : flowerbed[i - 1];
int next = i == len - 1 ? 0 : flowerbed[i + 1];
if (pre == 0 && next == 0) {
cnt++;
flowerbed[i] = 1;
}
}
return cnt >= n;
}
8. 判断是否为子序列
392. Is Subsequence (Medium)
s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc"
Return true.
public boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
int index = -1;
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
index = t.indexOf(c, index + 1);
if (index == -1) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
9. 修改一个数成为非递减数组
665. Non-decreasing Array (Easy)
Input: [4,2,3]
Output: True
Explanation: You could modify the first 4 to 1 to get a non-decreasing array.
题目描述:判断一个数组是否能只修改一个数就成为非递减数组。
在出现 nums[i] < nums[i - 1] 时,需要考虑的是应该修改数组的哪个数,使得本次修改能使 i 之前的数组成为非递减数组,并且 不影响后续的操作 。优先考虑令 nums[i - 1] = nums[i],因为如果修改 nums[i] = nums[i - 1] 的话,那么 nums[i] 这个数会变大,就有可能比 nums[i + 1] 大,从而影响了后续操作。还有一个比较特别的情况就是 nums[i] < nums[i - 2],修改 nums[i - 1] = nums[i] 不能使数组成为非递减数组,只能修改 nums[i] = nums[i - 1]。
public boolean checkPossibility(int[] nums) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length && cnt < 2; i++) {
if (nums[i] >= nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
cnt++;
if (i - 2 >= 0 && nums[i - 2] > nums[i]) {
nums[i] = nums[i - 1];
} else {
nums[i - 1] = nums[i];
}
}
return cnt <= 1;
}
10. 子数组最大的和
53. Maximum Subarray (Easy)
For example, given the array [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
the contiguous subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int preSum = nums[0];
int maxSum = preSum;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
preSum = preSum > 0 ? preSum + nums[i] : nums[i];
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, preSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
11. 分隔字符串使同种字符出现在一起
763. Partition Labels (Medium)
Input: S = "ababcbacadefegdehijhklij"
Output: [9,7,8]
Explanation:
The partition is "ababcbaca", "defegde", "hijhklij".
This is a partition so that each letter appears in at most one part.
A partition like "ababcbacadefegde", "hijhklij" is incorrect, because it splits S into less parts.
public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String S) {
int[] lastIndexsOfChar = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); i++) {
lastIndexsOfChar[char2Index(S.charAt(i))] = i;
}
List<Integer> partitions = new ArrayList<>();
int firstIndex = 0;
while (firstIndex < S.length()) {
int lastIndex = firstIndex;
for (int i = firstIndex; i < S.length() && i <= lastIndex; i++) {
int index = lastIndexsOfChar[char2Index(S.charAt(i))];
if (index > lastIndex) {
lastIndex = index;
}
}
partitions.add(lastIndex - firstIndex + 1);
firstIndex = lastIndex + 1;
}
return partitions;
}
private int char2Index(char c) {
return c - 'a';
}